Whether you create your own online advertising campaigns, or manage paid media for your clients, chances are that you’re familiar with Google’s suite of ad products. Google Ads (formerly AdWords) gives advertisers the opportunity to pay per click to display different types of digital advertisements within the Google Ads network.
With the pretty recent re-branding of Google’s advertising products in 2018, it’s more important than ever to stay on top of what has changed. By the end of the article, we hope you have a stronger understanding of Google Ads and feel confident to get started with (or improve) your campaigns.
What Does It Mean to Advertise Using Google Ads?
Google Ads is an advertising service that uses the pay-per-click (PPC) model of online advertising. PPC advertising is basically when users post ads on an ad platform and pay a fee to the platform’s host (in this case, Google) every time their ads are clicked.
The end goal is to drive an advertiser’s target audience to respond to a call to action (or in the best case, make a purchase) on his or her website.
A search engine like Google is an ideal place for businesses to advertise. Google allows advertisers to display ads that are the most relevant to users’ search intent with its Google Ads real-time keyword bidding technology.
How Paid Search Works
The process of “keyword bidding” starts whenever a user searches for something on Google. For example, let’s say someone is shopping for women’s denim jackets.
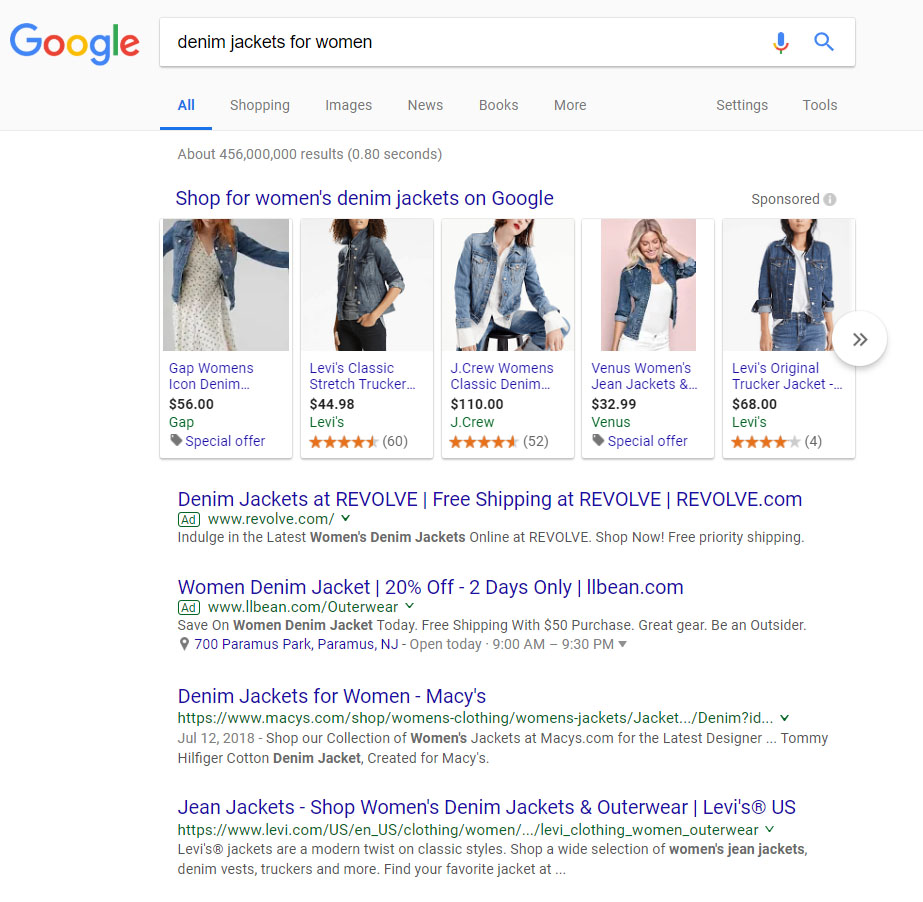
Notice how the first 2 search results after the 5 Google Shopping product listings are also paid ads. Every time there is a spot for an ad on Google’s SERP (search engine results page), competing bidders automatically fight for their product/service to appear for the relevant, popular keyword.
How to Win A Bid for Ad Placement
Your ad’s placement is determined by your Ad Rank, which is an algorithmic calculation heavily based on your bid amount, the ad’s and associated landing page’s quality, and the ad’s relevancy for a particular spot.
The AdWords bidding system takes many factors into account to identify and reward quality ads. High quality ads are ads estimated to perform better by giving people who click on them exactly what they’re looking for quickly.
One way to determine your ad’s likelihood of getting a top ranking is by assessing your Quality Score, which Google defines as the 1-10 rating that is reported for each keyword in your account (calculated by estimating the quality of your ads and their landing pages). This Quality Score is pretty powerful, so even if you have a lower bid than your competitor, if your Quality Score is much higher, you could win the position.
Your Quality Score is just one contributing factor to your Ad Rank, which is the calculated value that actually decides your position in the search results.
Google’s AdWords Fundamentals course outlines the main contributing factors to ranking on their search engine results pages (SERPs) as follows:
– Your ad bid
– How relevant your ad is
– The impact of the ad formats you enable
– The probability that your ad will get clicked
– The estimated measure of how well your website gives users who click your ads a valuable experience
These ad auctions are fast-paced and competitive, but winning means your brand can appear at the top of the Google SERP for your desired keyword, meaning that it displays before even organic search results. Keeping your ad campaign profitable definitely requires a keen understanding of bidding strategy, which takes experience.
In our denim jackets example, leading brands such as Gap and Levi’s won the Google Shopping ad placements, while other established brands such as Revolve and LL Bean won the two paid search results spots.
It makes sense that established companies are the ones who won these ad bids because their marketing budgets can afford to bid on more expensive, competitive search terms, like “denim jackets for women”.
How to Optimize Your PPC Ads
Even if you win the top position, a PPC ad can be a waste of time and money if it isn’t optimized properly. Running a profitable PPC ad campaign is definitely possible, as long as you make sure you do at least the following:
1) Make sure the copy for your ads is perfect.
You might want to hire an expert for this, because designing PPC ads and writing text requires a specific skill and familiarity with what will perform best. Google Ads provides an extremely limited amount of space to grab people’s attention and make them click, you need a clear, foolproof call to action (CTA). Emphasize what makes your product/service/overall brand stand out. You don’t need to be the most creative, but you need to communicate clearly and have a hook (for example a special offer). Always use strong verbs when you can, because “Contact Us” and “Call Today” are extremely cliche and boring.
2) Emphasize your location.
If you have more than one location, it’s imperative for you to make a different PPC campaign for each town or geographic region if you want to get the most clicks possible on your ads. When people who are looking for something online, they often go for whatever business seems the most approachable and accessible.
Convenience is a major driving factor for people’s buying behavior. If you’re an ecommerce business without a brick and mortar location, it might be smart to highlight convenient free or fast shipping or customer support. If you’re competing with a local business that has more of a chance of making a memorable first impression, your brand needs to take the next step so that you don’t become another faceless, transactional business.
3) A/B split test your ads.
Sometimes a small tweak in design or copy can make a difference of hundreds of clicks. The problem is when you aren’t able to identify what works and what doesn’t work. If you are regularly A/B split testing your PPC ads, you’ll be able to make them the most effective possible. The more information you have about how different versions of your ads are performing, the better. Collect and track this data to figure out what is the most ideal options for the wording of your ad, the place of your call to action, the placement of numbers and statistics, links, and the benefits of your product/service.
4) Use ad extensions.
More on this in the next section.
How to Use Ad Extensions to Your Advantage
An ad extension is a great way to improve the click through rate (CTR) of your PPC ads. All an ad extension does is provide additional information or a stronger call to action. Your ad needs to be solid to start, but an ad extension can give it a competitive edge.
As you can see below, LL Bean specifies its nearest store location and hours in an extension for its ad for women’s denim jackets.
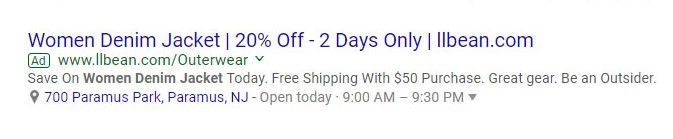
There are multiple extension formats, and there are both manual and automatic ad extensions. You need to set up manual extensions yourself, whereas automatic extensions are applied by default whenever specific conditions are met.
Below we’ll list the different kinds of manual extensions and automatic extensions frequently used by PPC advertisers on Google Ads.
Manual Ad Extensions
1) Sitelinks
You can add links underneath your meta description to take people to specific pages within your site.
2) Callout ad extensions
Callouts underscore specific information, such as special benefits, about your business’s products or services.
3) Structured snippet ad extensions
Structured snippets allow you to highlight certain differentiating features of whatever product/service you’re promoting. For example, if you’re a gym you could include the amenities of the equipment, pool, sauna, etc.
4) Call extensions
These extensions enable advertisers to add phone numbers to their ads. Only do this is you actually have a sales/customer service team to answer the calls.
5) Message extensions
Similar to call extensions, these extensions enable searchers to contact a business via text message. It’s usually smart to connect your message extension to some kind of third party chat software so that you’re not bombarded by a n influx of messages you can’t answer.
6) Location extensions
These extensions are exactly what they sound like: an add-on that helps searchers find your physical business location. The LL Bean extension is a perfect example. You can even ensure people can click to find directions to your business on Google Maps.
7) Affiliate location extensions
These extensions allow searchers to find exactly where to purchase your products in a physical retail store near them. If you’re a retail chain or auto dealer, this is for you.
8) Price extensions
These extensions appear below your ad and show specific products and pricing information that a searcher would want to know.
9) Promotion extensions
Usually these kinds of extensions are only available for advertisers to use in certain countries (they’re not universally available). Basically, a promotion extension allows advertisers to emphasize sales/special offers in their ads. You emphasize the special promotion using a bold label such as “Deal” or “Seasonal sale”.
10) App extensions
Extensions that allow advertisers to directly link to your mobile app in the ad.
Automatic Ad Extensions
Note: Although these extensions populate automatically, you can always opt out of them.
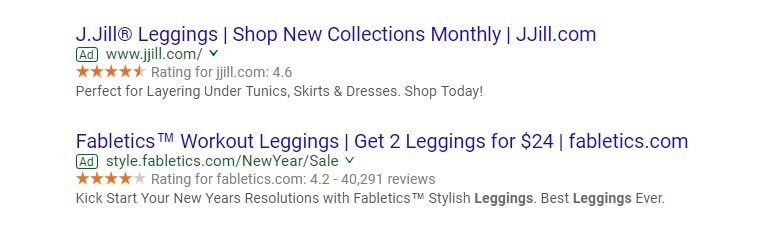
1) Seller rating extensions
These are the star ratings you oftentimes see under a PPC ad’s title. If your business gets consistently high ratings, it makes sense to automatically highlight this selling point. These ratings show a combination of information and reviews. One reason why advertisers love these extensions is because you aren’t charged for clicks on seller rating extensions. Here are two examples:
- Dynamic callouts
- Dynamic structured snippets
- Dynamic sitelink extensions
- Automated call extensions
- Automated message extensions
- Automated location extensions
Overview of Google Ads Formatting and Targeting Options
The various PPC ad formats that Google Ads offers can be split into two broad categories:
Those that you see on Google’s SERP
Those that display across the web
When you use Google Ads, it’s incredibly easy to advertise across channels and formats. Especially with the new Google Ads rebrand, the digital advertising experience is designed to connect everything from search to display to video ads so you can create a more seamless campaign.
The targeting options available for PPC advertising across Google’s ad network is impressive. The 5 broad categories of targeting options can be divided as follows:
1) Search Targeting
2) Display Targeting
3) Contextual Targeting
4) Audience Targeting
5) Remarketing
To Wrap It Up…
In future posts, we’ll delve further into the details of what it takes to run a profitable and highly targeted PPC ad campaign. Google makes it possible to deliver extremely targeted messages based on your audience’s search behavior and the kinds of content they view regularly.
At Chainlink, our team of experts can help you get the most out of every dollar you spend on paid advertising. We have experience running Google Ads campaigns with a wide range of clients with unique needs.
Using search, display, retargeting ads and more, we can make sure your website is attracting the widest relevant audience possible to fill your sales funnel with new prospects. We understand that each PPC ad budget is different and we enjoy finding creative ways to get you the most for your money.